French Chansons Composed by Ernest Chausson

Ernest Chausson, by Guy & Mockel, Paris (ca. 1897)
French composer Ernest Chausson’s early death in a bicycle accident cut short a career just as it was beginning to flourish. His position as secretary of the Société Nationale de Musique for 13 years put him at the centre of France’s active music networks. He studied with Massenet and César Franck at the Paris Conservatoire, which he attended at the relatively advanced age of 24, was friends with Vincent d’Indy, and many other composers including Henri Duparc, Gabriel Fauré, Claude Debussy, and Isaac Albéniz. He also knew the poet Mallarmé, although he never set any of his poetry, and the painter Monet.
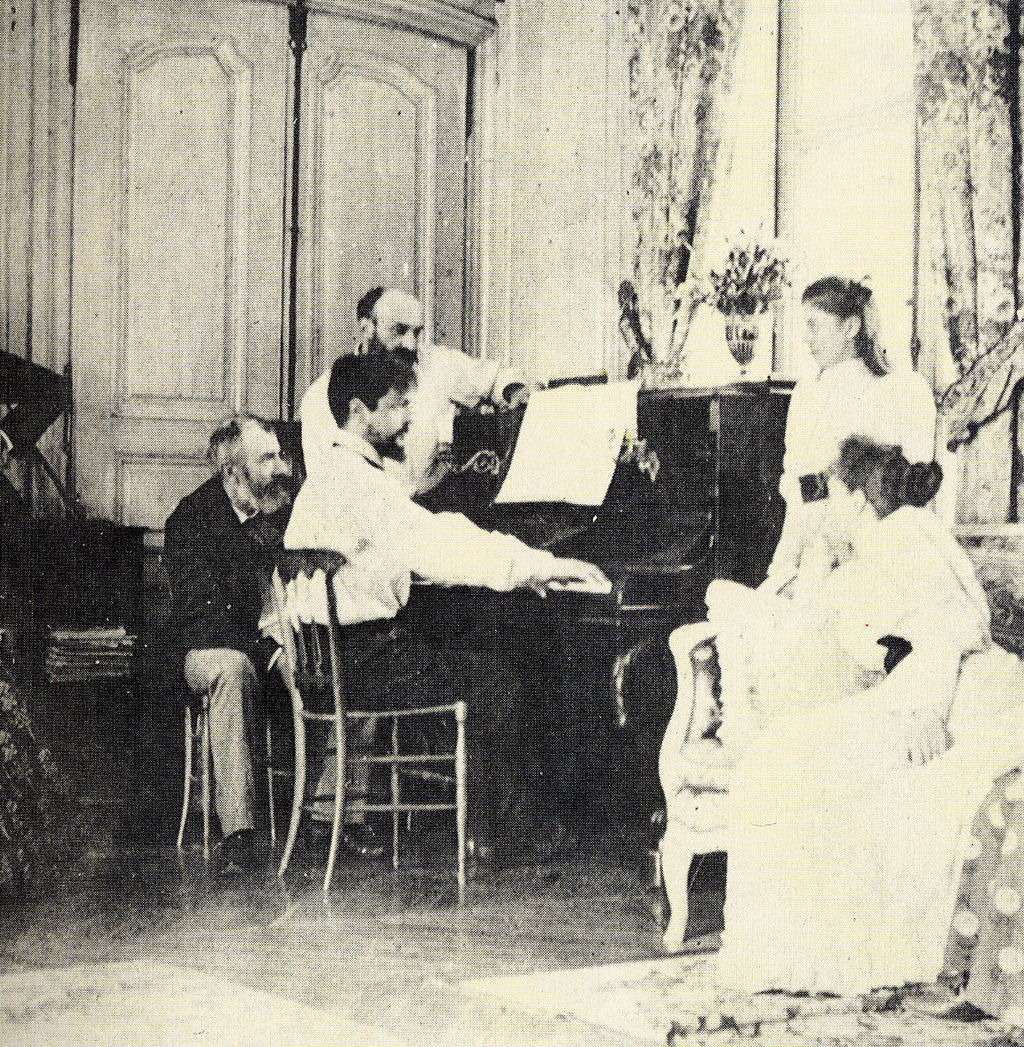

Chausson, standing, turning pages for Debussy (1893)
The poets he set include Camille Mauclair (1872-1945), Jean Richepin (1849-1926), Alfred de Musset (1810-1857), Leconte de Lisle (1818-1894), Maurice Bouchor (1855-1929), and Maurice Maeterlinck (1849-1949), among others. If we look just at his contemporaries, Camille Mauclair, Maurice Bouchor, and Maurice Maeterlinck, we have three poets of very different sensibilities.

Camille Mauclair by Lucien Lévy-Dhurmer (1896)
Camille Mauclair (the pseudonym of Séverin Faust) was not only a poet but also a novelist, biographer, travel writer, and critic. He was an admirer of Mallarmé and was most famous for his roman à clef, Le Soleil des Morts (1898). For his contemporaries, it was brilliant portrait of the leading actors in the arts of his day, including writers, artists, critics, and musicians. For us, it has become an important historical document about the French avant-garde at the end of the nineteenth century. One of the most musically relevant portraits in the novel is that of Debussy at the premiere of “Prélude à L’Après-midi d’un faune”. Chausson appears in the book as ‘Rudolphe Méreuse’ and is the dedicatee of the novel. He is, in the novel, praised as ‘ …the composer whose symphonies, with those of César Franck, were the only original works to appear since Wagner.’
Mauclair provided the words for Chausson’s Op. 27 lieder. The first song, Les heures, casts us directly into the shadowy decadent world of the French fin du siècle: the piano provides a mordent background to the poet, ‘singing until death’ the pale hours of the night.
Ernest Chausson: 3 Lieder, Op. 27 – No. 1. Les heures (Brigitte Balleys, mezzo-soprano; Billy Eidi, piano)

Maurice Bouchor
Maurice Bouchor was a poet and playwright with an interest in music. He worked with the musician Julien Tiersot to preserve French folk songs and published a book of them for use in schools.
His poetry was set extensively, and Chausson set it a number of times, most memorably in his Op. 8 set. This set of four poems describes love in all aspects: from the young love in the first poem, the memory of a former lover in the second, to the broken heart of ‘Printemps triste’ and the memories of the happy past in ‘Nos souvenirs’.
Ernest Chausson: Quatre Melodies – No 3. Printemps triste (Jean-Francois Gardeil, baritone; Billy Eidi, piano)

Maurice Maeterlinck
The Belgian playwright, poet and essayist Maurice Maeterlinck was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1911. At the end of the 19th century and into the early 20th century, he was a source of musical inspiration: Debussy set his Pelléas and Mélisande, and it inspired Gabriel Fauré, Arnold Schoenberg, Jean Silbelius and others. 13 of his other plays were also made into operas, inspired symphonic poems, or had incidental music written for them by some 40 composers. His plays forged a new style, an example of which can be seen in Pelléas and Mélisande: the setting is lean and spare and the characters have no foresight and a limited view and understanding of themselves and the world they inhabit. The forces that compel people, not the emotions that drive them, was the centre of his style.
Maeterlinck’s first collection of poetry, Serres chaudes (Hothouses) (1889), was the source for Chausson’s Op. 24 song cycle. The second song, ‘Serre d’ennui’ (Hothouse boredom), seems to capture the overly humid confines of a hothouse, where boredom is blue but is captured within a green world where all is still.
Ernest Chausson: Serres chaudes, Op. 24 – No. 2. Serre d’ennui (Isabelle Druet, mezzo-soprano; Johanne Ralambondrainy, piano)
Chausson set poetry by many other poets, including Verlaine, Baudelaire, Leconte de Lisle, and Gautier. In his brief life, Chausson brought the French chanson forward out of the Romanticism found in composers such as Massenet and Franck and closer to the more introspective world found in Debussy’s work.
For more of the best in classical music, sign up for our E-Newsletter